44 egg structure with labels
Structure of the Gametes - Colorado State University Structure of the Gametes Before Fertilization. Fertilization presents some major challenges to both sperm and egg: The fertilizing sperm must somehow recognize, bind to and ultimately traverse the zona pellucida surrounding the egg. It then must bind to the plasma membrane of the egg. The egg must not only respond to the fertilizing sperm in a ... Egg labels - the complete guide; how to understand them The egg labels, respectively the egg markings may contain a number of information, such as the country code and the producer code (for eggs sold in the EU) and the method of production. In the EU, the method of production is indicated through a numbered system. Egg labeling is used worldwide, mostly in the form of labels for egg cartons.
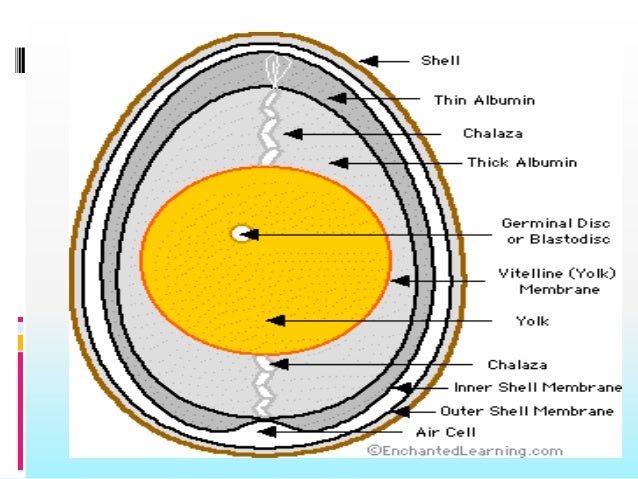
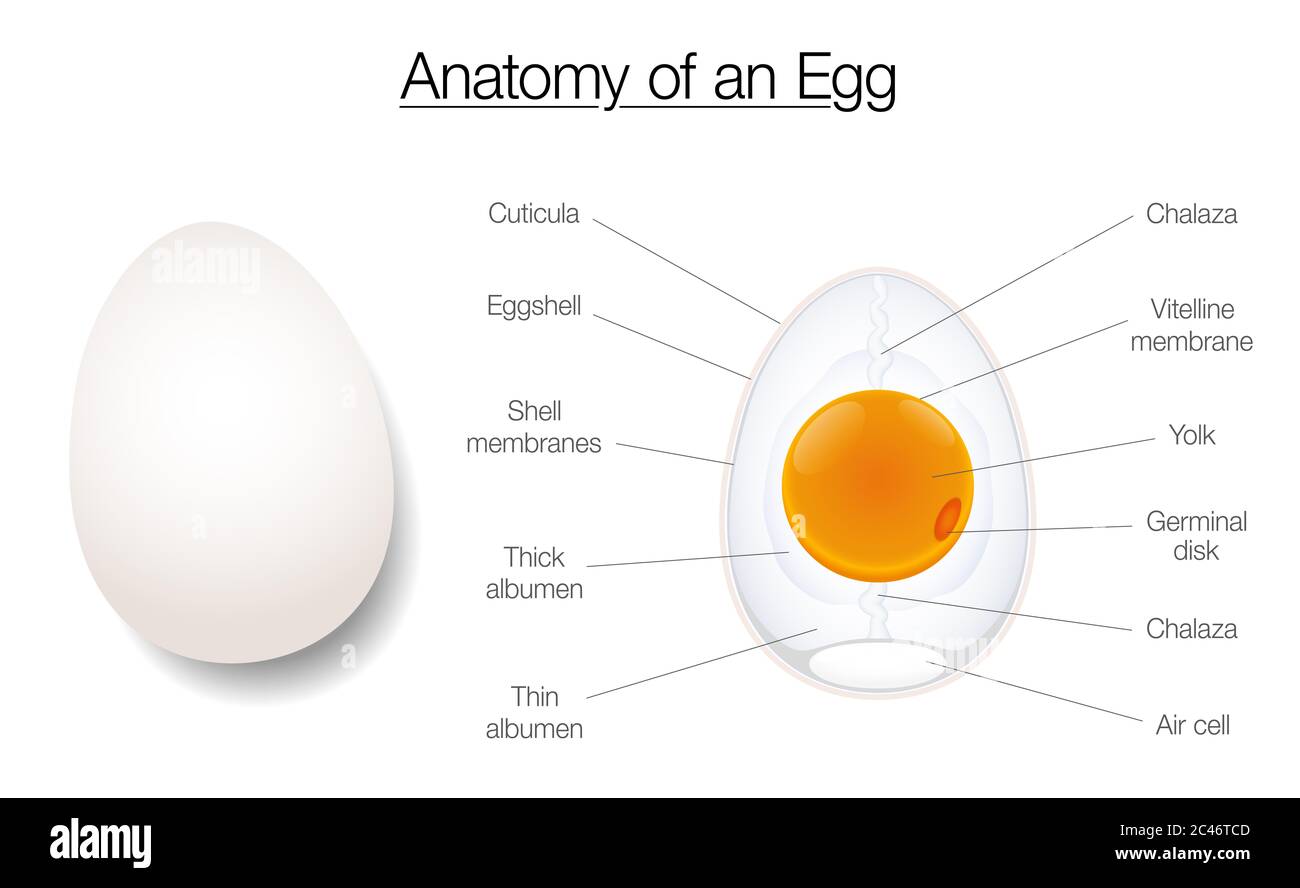
The Anatomy of an Egg: We Take a Closer Look - Hobby Farms The albumen is packed with protein—about 40 proteins, actually—while the rest is water. It includes four sections: the outer thin, the outer thick, the inner thin and the inner thick. The albumen connects to the yolk and shell with two cords called chalazae.

Egg structure with labels
Illustrating the Layers of the Earth Through Egg Dissection This simple activity requiring only boiled eggs models the 3 layers of the Earth. It is most appropriate for elementary students but can be utilized with variations (See below) for middle school students. Pictures by Ditmar Hospitál Preparation: Boil 1 egg per student. It is a good idea to boil an extra egg in case one breaks. Materials Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Science of Cooking 14. Air cell -- An air space forms when the contents of the egg cool and contract after the egg is laid. The air cell usually rests between the outer and inner membranes at the egg's larger end. As the egg ages, moisture and carbon dioxide leave through the pores of the shell, air enters to replace them and the air cell becomes larger. 15. The Human Egg Cell | Egg Donation | Altrui What is the structure of an egg cell? Above you will see a diagram that labels the main parts of the human egg cell, together with an illustration of a real human egg. Nucleus: the nucleus is the heart of the egg cell; it contains most of the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. This is where the genes are situated.
Egg structure with labels. Label Chicken Egg (#1) Printout - EnchantedLearning.com Label the Chicken Egg (#1) Label the cross section of a newly-laid chicken egg. Chickens Bird Printouts air cell - an empty space located at the large end of the egg; it is between the inner and outer shell membranes. chalaza - a spiral, rope-like strand that anchors the yolk in the thick egg white. Clean Label Egg Replacement - Ulrick & Short We have over 20 years of food industry knowledge and expertise in clean label ingredient development. We work with manufacturers like you to overcome the most difficult product formulation challenges from reducing fat and sugar, replacing egg and removing phosphates to improving product stability, texture and appearance. Structure of the Egg - Incubation and Embryology - University of ... Surrounding the albumen are two shell membranes and the shell itself. The shell contains several thousand pores that permit the egg to "breathe." Composition An average-sized egg weighs approximately 57 grams (about 2 ounces). Of this weight, the shell constitutes 11 percent; the white, 58 percent; and the yolk, 31 percent. The Different Parts of an Egg | Sauder's Eggs Eggs can be categorized into seven volumes, with jumbo and large eggs the highest commercially sold and most referenced throughout recipes. An egg's weight also includes the net mass of the entire makeup, including its shell. Shell Color: Chicken eggs come in a rainbow of colors, from blues and greens to whites, browns, and even speckled varieties.
Chicken egg structure ( in simple way) - YouTube In this video I have explained about chicken egg structure in a simple way.. Thank uhttps:// ... Types of Eggs - The Spruce Eats Here are some of the most common. Fried eggs (which includes styles like over-easy and sunny side up) Scrambled eggs. Poached eggs. Boiled eggs ( hard-boiled and soft-boiled) Shirred or baked eggs. Frittatas and omelets. Eggs are also used in emulsified sauces like mayonnaise, Hollandaise and others. Science of Eggs: Anatomy of an Egg | Exploratorium An air space forms when the contents of the egg cool and contract after the egg is laid. The air cell usually rests between the outer and inner membranes at the egg's larger end, and it accounts for the crater you often see at the end of a hard-cooked egg. The air cell grows larger as an egg ages. The egg white is known as the albumen, which ... Structure of the Amniotic Egg Evolution of eggs with a water-impermeable amniotic membranesurrounding a fluid-filled amniotic cavity permits embryonic development on land without danger of dessication. The main diagram shows the arrangement of membranes in a typical egg-laying oviparousvertebrates. In live-bearing viviparousvertebrates, the shell and chorionic
Solved The structure indicated by Labels A and B are | Chegg.com the structure indicated by labels a and b are responsible for: production of adh and oxytocin that are released into the anterior pituitary production of fsh and lh that are released into the interior pituitary production of fsh and tell that are released into the posterio pintar production of adh and oxytocin that are released to the posterior … Solved In the sketch of the structure of NF3 label all | Chegg.com In the sketch of the structure of NF3 label all bonds. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help o: N(p) - F(p) T: N(P) - F(p) 11 O: N(P) - F(sp) T. : N(spl) - F(p) Lone pair in p orbital Lone pair in sp orbital Lone pair in 8 orbital a : N(sp) - F(p) Structure of the egg - HEDEGAARD - DAVA An egg basically consists of three parts: a shell an egg white an egg yolk An egg from a hen consists of approximately 2/3 egg white and 1/3 egg yolk. The eggshell The shell is built of 8-10,000 pores, which ensures that oxygen can penetrate and CO 2 and other gases can escape. What Do the Labels on Egg Cartons Actually Mean - Lifehacker Grade AA, grade A, grade B - Grading measures egg "quality" according to the USDA. Eggs are downgraded for having air cells, blood spots, or "serious yolk defects." You can read the criteria here....
label parts of a cell yolk is surruondedby the substance called - Science - Cell - Structure we have 9 Images about yolk is surruondedby the substance called - Science - Cell - Structure like Parts and Function of Digestive System for Med School & Nursing, 2.4.1 Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes - YouTube and also Connective tissue - BIOLOGY4ISC.
Egg structure. Anatomy of a birds egg, labeled chart with names of the ... Download this stock image: Egg structure. Anatomy of a birds egg, labeled chart with names of the components - diagram illustration on white background. - 2C46TCD from Alamy's library of millions of high resolution stock photos, illustrations and vectors.
The Structure of the Egg. Ovum Anatomy. Vector Illustration on Isolated ... Human Egg or Ovum structure and Human Sperm or Spermatazoa for health education infographic. Vector illustration of ovum and sperm cell. More stock photos from Iryna Timonina's portfolio. Obstruction of the fallopian tubes. The structure of the pelvic organs. Infographics. Vector illustration on isolated
PDF Egg Parts - University of Illinois Extension Color each part of the egg a different color and label each part of the egg. Use each word only once: air cell germinal disc vitelline membrane albumen or white membranes yolk chalaza shell albumen or white shell KEY air cell yolk chalaza vitelline membrane membranes germinal disc. Title: Embryology Worksheets Author: OUP
Egg: Definition, Structure and Classification - Your Article Library Eggs can be classified into different types as discussed in Table 14.1: 1. Chicken eggs: These are the most commonly eaten eggs around the world. They are available in brown colour and white colour. The brown coloured ones are referred to as desi eggs in India. 2. Duck eggs: They are darker in colour than chicken eggs and are larger in size too.
draw and label the structure of egg - Brainly.ph draw and label the structure of egg - Brainly.ph. johnreytorio2. 21.10.2020. Technology and Home Economics. Senior High School.
Structure of The Egg - DAVA Foods Structure of the egg An egg basically consists of three parts: a shell, an egg white and an egg yolk. An egg from a hen consists of approximately 2/3 egg white and 1/3 egg yolk. Bacterial retardant
The Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Parts and Functions of an Egg An eggshell is a semipermeable membrane, allowing air and moisture to pass the pores. Bloom or Cuticle It is a thin outermost coating of the eggshell which keeps out dust and bacteria. It keeps out the dust by sealing the pores on the eggshell. This also reduces moisture loss from the interior of the egg. Outer and inner shell membranes
Physical Structure and Composition of an Egg - Prezi Chalaza. This is the ropey strands of egg white at both sides of the egg, which anchor the yolk in place in the center of the thick white. Accounts for most of an egg's liquid weight, about 67%. This is produced by the oviduct and consists of four alternating layers of thick and thin consistencies.
The Parts of the Egg - Virginia Tech In a fresh egg, we can see white cords attached to the yolk sac. These two cords, called chalazae, are made of twisted strands of mucin fibers that are a special form of protein. The chalazae hold the yolk in the center of the egg. The yolk is the source of food for the embryo and contains all the fat in the egg.
The Human Egg Cell | Egg Donation | Altrui What is the structure of an egg cell? Above you will see a diagram that labels the main parts of the human egg cell, together with an illustration of a real human egg. Nucleus: the nucleus is the heart of the egg cell; it contains most of the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. This is where the genes are situated.
Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Science of Cooking 14. Air cell -- An air space forms when the contents of the egg cool and contract after the egg is laid. The air cell usually rests between the outer and inner membranes at the egg's larger end. As the egg ages, moisture and carbon dioxide leave through the pores of the shell, air enters to replace them and the air cell becomes larger. 15.
Illustrating the Layers of the Earth Through Egg Dissection This simple activity requiring only boiled eggs models the 3 layers of the Earth. It is most appropriate for elementary students but can be utilized with variations (See below) for middle school students. Pictures by Ditmar Hospitál Preparation: Boil 1 egg per student. It is a good idea to boil an extra egg in case one breaks. Materials



![Eggshell Carving Art [25 Pic] ~ Awesome Pictures](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhS5UuBQqri-_e9-ZjmKhFr7wx64ljLGJ1vE_49ucgmWgB7yh9fCCjZL1QdCz0BPS8Xpf9_rh-bncxf8QlGXXNDxXEHXK7u69dy62QQNRDeWWJSIZBjtF0OIiU7J8gAEMesforCnlcWNm8/s1600/eggshell+carving+art+2.jpg)




Post a Comment for "44 egg structure with labels"